It is important to choose a reliable hosting service as it can impact various resources such as finance, reputation and time. There is no doubt that the first step in research is defining the requirements (location, hardware, price, etc.) for a hosting solution. Knowing what you want is half the battle.
Here's a guide on the aspects to consider when choosing a hosting service that meets your business or personal needs.
Table of Contents
1.  Business
Business
First of all, hosting is a business, so try to do some quick research about the company and its related information.
-
company
-
registration
is the hosting company a registered company? Check it's registration number.
-
year of foundation
check the year the company was founded, new companies are at a higher risk
-
country
(office location, company address)
according to the company location, some risks can be sanctions, conflict zones, etc.
-
team and CEO
(the team or career page, the information on the LinkedIn page and GitHub account)
a fake team, or a company that relies on just one person (bus factor: 1), can lead to several problems in the future
-
telecommunications license
having a telecommunications license is a positive indicator for the company
-
registration
-
contacts
(technical/sales/abuse departments email, phone, working hours)
test the response times by using live chat, sending an email, creating tickets, and calling by phone if available; no phone option may be suspicious, but it is not a red flag
-
news, social media accounts (X/twitter)
explore how actively the company introduces something new
-
reviews and reputation
-
internet platforms
(Web Hosting Talk, LowEndTalk, Reddit, Hacker News...)
some reviews on platforms like Trustpilot may be fake; also it happens that non-standard issue can be resolved by mentioning the company on Reddit and HN
- friends and colleagues
-
internet platforms
(Web Hosting Talk, LowEndTalk, Reddit, Hacker News...)
- website
-
domain
(creation date, registrant, NS servers,..)
using whois utility
-
web server location
(country, data center)
using Check-Host Info for example
- SSL certificate information (Organization Validation)
-
domain
(creation date, registrant, NS servers,..)
2.  Data centers
Data centers
A data center is the physical location where servers are housed. A company may operate multiple data centers and host servers in different locations. Therefore, the company's business address is not necessarily the same as the location of its servers.
-
location
(country, city)
sometimes a server should be as close to your other servers as possible; in some cases, the location of a server can introduce political risks; and depending on requirements, it may be undesirable to have a server located in a country that is part of the "Fourteen Eyes" alliance...
-
ownership
is the data center owned by the hosting company itself? Owning a data center usually allows for quick incident resolution.
-
Tier number
it indicates different types of data center infrastructure, including maintenance, power, cooling, and fault tolerance. The highest classification level is Tier IV.
-
data center location specifics
AUP (Acceptable Use Policy) can vary (VPN and torrents may be prohibited), DDoS protection can be different, etc.
-
photos/video
photos and videos from the data center can provide a quick impression of what it looks like inside and service quality
-
history of the data center
the year it was built, any past accidents, and so on
You can find more information about data centers in catalogs: https://www.datacentermap.com, https://datacentercatalog.com, https://www.datacenters.com
3.  Network
Network
The network is the most critical factor for ensuring reliable hosting.
-
ASN (Autonomous System Number)
get info about upstreams, peering, IPv6 support using test IP address or organization/data center name at bgp.tools, dns.he.net, peeringdb websites; does company have a BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) network blend or even a single homed? A BGP network automatically reroutes traffic away from a problematic Internet Service Provider (ISP) to another ISP.
-
IP addresses
IPv4 and IPv6 support, number of IPs for a server, price for additional IPs, failover IP address option...
-
network status over status page
check the current status, any downtimes, and responses to past incidents, example: Linode network status page
-
blocked ports
for example, outgoing mail ports such as 25 and 465 may be blocked
-
bandwidth limits and port speed
check the limits and additional charge
-
DDoS protection
protection speed limits, mitigation methods, failover IP option, black hole (null route) policy, fees and etc.; typically, large companies offer basic DDoS protection at no cost
- network test
-
LG (looking glass)
ping/trace a specified IP address from hosting's servers, LG example: Twelve99 Looking Glass
-
ping from multiple locations
check the latency from different countries using Check-Host Ping
-
speed test pages
examples: Linode speedtest page and OVH speedtest page
-
system utilities
ping, traceroute, mtr, wget, iperf
-
speed test benchmarks
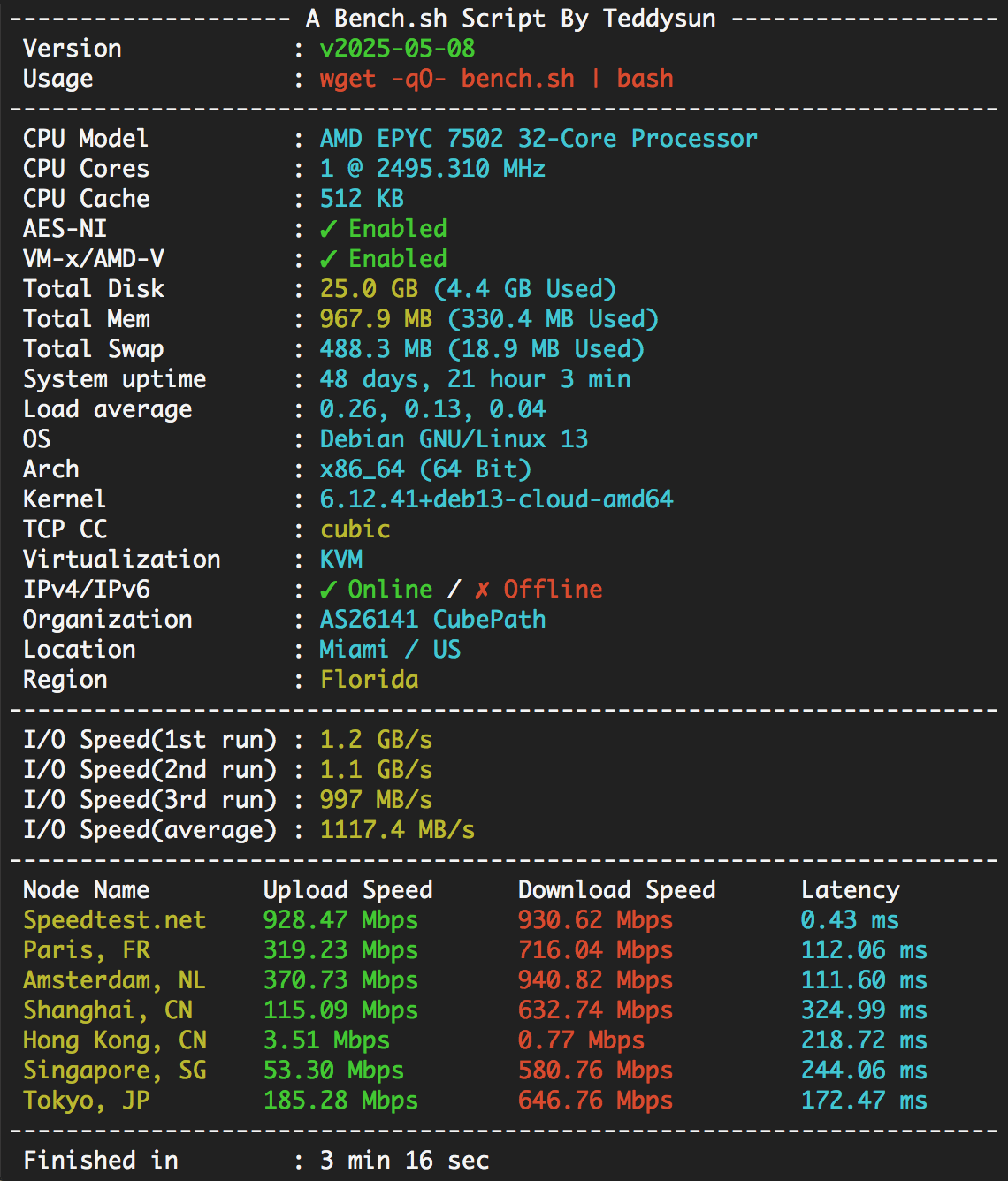
Output of speedtest-cli:
Retrieving speedtest.net server list... Selecting best server based on ping... Hosted by Suomi Communications Oy (Espoo) [15.66 km]: 1.817 ms Testing download speed... Download: 250.68 Mbit/s Testing upload speed... Upload: 305.94 Mbit/sbench.sh report example ▾
-
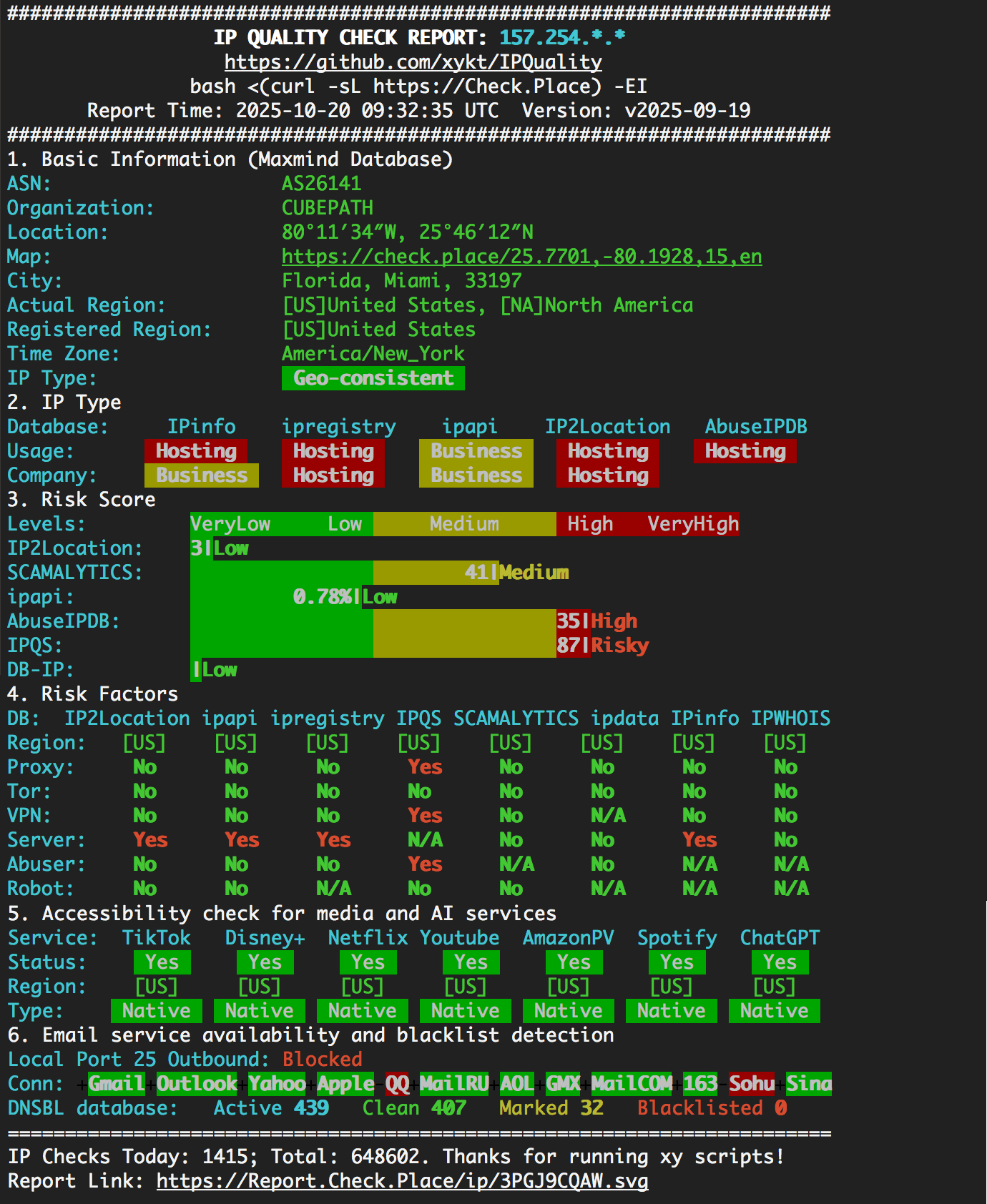
IP address reputation
check IP address geographical location information, blacklisting, risk score and factors (using IPQuality for example)IP Quality Check Script output ▾
-
LG (looking glass)
4.  Hardware
Hardware
Hardware parameters are mostly related to CPU (speed and cores), memory (type and capacity), and disk (type, speed, capacity).
-
specifications
check the hardware specifications: is the hardware old or modern
-
upgrade
available upgrades/downgrades (memory upgrade, adding disks, and etc...)
-
features for dedicated servers
available OS, RAID types (software, hardware), IPMI, IPKVM (KVM-over-IP), Rescue Mode...
-
setup time
for dedicated servers, it can take from a few minutes to 1-3 days
-
ownership and maintenance
hosting company may either own the hardware in their data centers or rent it, which can vary by location. In the case of reselling, this can often lead to outages, especially when it comes to replacing failed hardware such as power supplies or disks. Additionally, issues like service suspension and network limit upgrades can also cause disruptions.
-
real benchmark test
run a real benchmark on the server to know the true capabilities of hardware, for example using YABS (yet-another-bench-script)Yet-Another-Bench-Script output example ▾
# ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## # # Yet-Another-Bench-Script # # v2024-12-17 # # https://github.com/masonr/yet-another-bench-script # # ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## # Thu Dec 15 09:45:10 UTC 2024 Basic System Information: --------------------------------- Uptime : 33 days, 10 hours, 15 minutes Processor : AMD EPYC-Milan Processor CPU cores : 32 @ 2399.998 MHz AES-NI : ✔ Enabled VM-x/AMD-V : ✔ Enabled RAM : 61.3 GiB Swap : 0.0 KiB Disk : 393.7 GiB Distro : Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookworm) Kernel : 6.8.12-4-pve VM Type : NONE IPv4/IPv6 : ✔ Online / ✔ Online IPv6 Network Information: --------------------------------- ISP : OVH SAS ASN : AS16276 OVH SAS Host : OVH Location : Gravelines, Hauts-de-France (HDF) Country : France fio Disk Speed Tests (Mixed R/W 50/50) (Partition /dev/sda1): --------------------------------- Block Size | 4k (IOPS) | 64k (IOPS) ------ | --- ---- | ---- ---- Read | 323.10 MB/s (80.7k) | 2.05 GB/s (32.1k) Write | 323.96 MB/s (80.9k) | 2.06 GB/s (32.3k) Total | 647.06 MB/s (161.7k) | 4.12 GB/s (64.5k) | | Block Size | 512k (IOPS) | 1m (IOPS) ------ | --- ---- | ---- ---- Read | 2.33 GB/s (4.5k) | 2.39 GB/s (2.3k) Write | 2.45 GB/s (4.7k) | 2.55 GB/s (2.4k) Total | 4.78 GB/s (9.3k) | 4.94 GB/s (4.8k) iperf3 Network Speed Tests (IPv4): --------------------------------- Provider | Location (Link) | Send Speed | Recv Speed | Ping ----- | ----- | ---- | ---- | ---- Clouvider | London, UK (10G) | 3.91 Gbits/sec | 3.92 Gbits/sec | 5.08 ms Eranium | Amsterdam, NL (100G) | 3.90 Gbits/sec | 3.88 Gbits/sec | 11.1 ms Leaseweb | Singapore, SG (10G) | 1.10 Gbits/sec | 834 Mbits/sec | -- Clouvider | Los Angeles, CA, US (10G) | 1.23 Gbits/sec | 1.28 Gbits/sec | 138 ms Leaseweb | NYC, NY, US (10G) | 1.63 Gbits/sec | 2.47 Gbits/sec | -- Edgoo | Sao Paulo, BR (1G) | 802 Mbits/sec | 916 Mbits/sec | 185 ms iperf3 Network Speed Tests (IPv6): --------------------------------- Provider | Location (Link) | Send Speed | Recv Speed | Ping ----- | ----- | ---- | ---- | ---- Clouvider | London, UK (10G) | 3.86 Gbits/sec | 3.86 Gbits/sec | 4.24 ms Eranium | Amsterdam, NL (100G) | 3.84 Gbits/sec | 3.82 Gbits/sec | 10.1 ms Leaseweb | Singapore, SG (10G) | 404 Mbits/sec | 991 Mbits/sec | 161 ms Clouvider | Los Angeles, CA, US (10G) | 960 Mbits/sec | 1.28 Gbits/sec | 137 ms Leaseweb | NYC, NY, US (10G) | 2.18 Gbits/sec | 2.40 Gbits/sec | 76.2 ms Edgoo | Sao Paulo, BR (1G) | 734 Mbits/sec | 913 Mbits/sec | 184 ms Geekbench 6 Benchmark Test: --------------------------------- Test | Value | Single Core | 2007 Multi Core | 16712 Full Test | https://browser.geekbench.com/v6/cpu/xxxxxx YABS completed in 10 min 57 sec
5.  Technologies and add-ons
Technologies and add-ons
Some add-ons and technologies may be necessary based on your needs, while others are good to have:
-
virtualization technology
(KVM, Xen, Hyper-V, OpenVZ...)
OpenVZ has some limitations, and today KVM is mostly used
-
scalability
scalable hosting gives you flexibility and control to scale up resources (processing power, memory, and bandwidth) to handle the increased load
-
cloud solutions
cloud storage, load balancers, serverless applications, container orchestration solutions (Kubernetes) and etc.
-
firewall
in some cases, a dedicated firewall can be a very useful option for enhancing protection capabilities during network attacks
-
backups
automatic backups, snapshots, easy and quick recovery; it is also better to keep a copy of backups in an alternative data center of another hosting provider
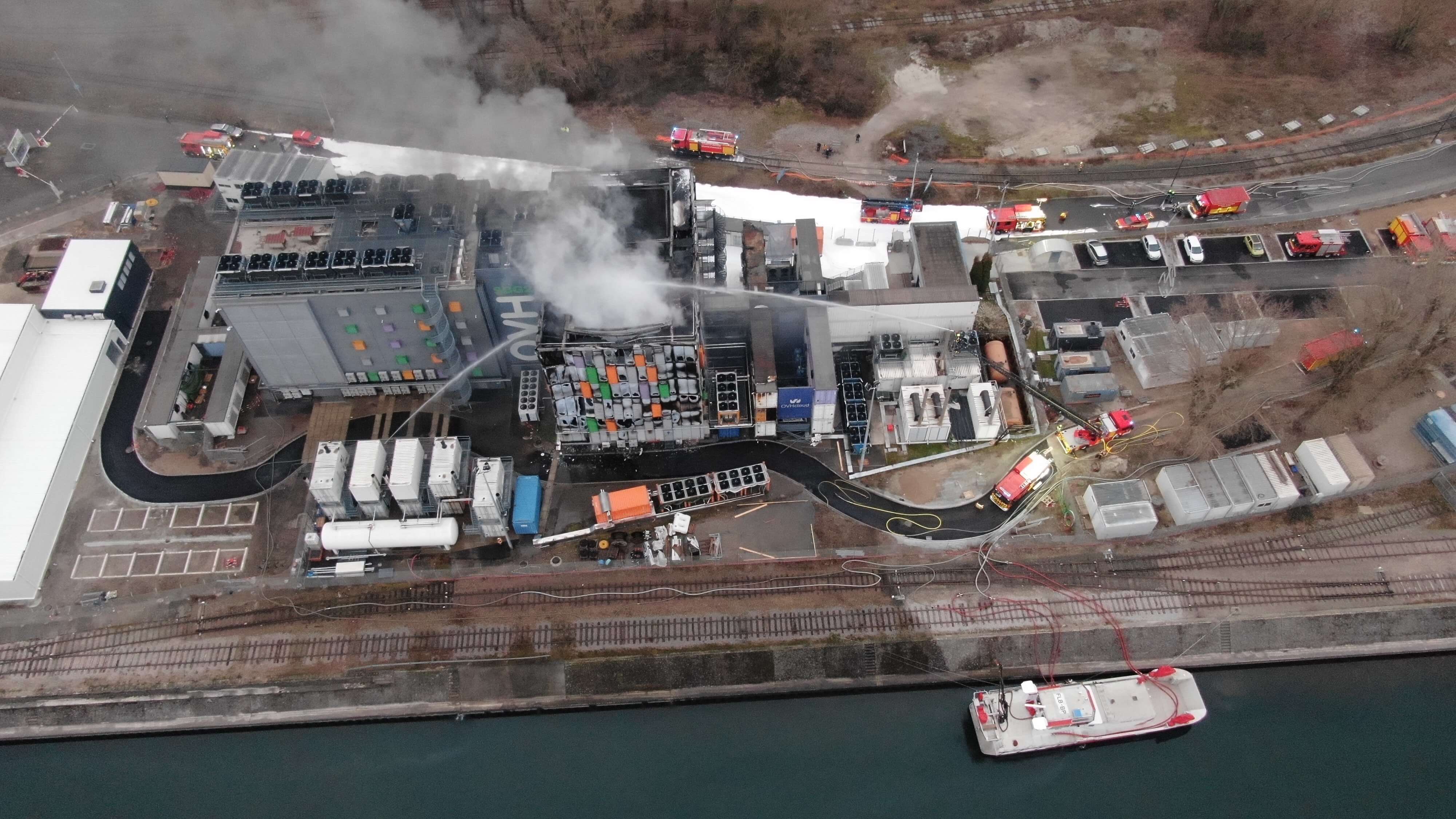 Fire at OVH data center in Strasbourg, March 2021
Fire at OVH data center in Strasbourg, March 2021
6.  Terms Of Use
Terms Of Use
Review the Terms of Use and other legal documents for important information:
-
AUP (Acceptable Use Policy)
some hosting companies do not permit VPN, Tor, mail servers, torrent activities, etc. Their responses to incoming attacks, port scanning, and DMA violations can be quite strict.
- SLA (Service Level Agreement) uptime
- refund policy and money-back guarantee
- privacy policy
- other policies and agreements
7.  User experience
User experience
A smooth onboarding process helps get started quickly, and good software helps comfortably manage servers.
-
user registration and verification
phone verification and scans of certain documents may be required; sometimes, registration or payment is not possible from specific countries or when using a VPN
-
payments
payment options (cards, cryptocurrency and etc.), billing panel usage experience; during the payment process you can usually find the company's legal name and address on the payment gateway page
-
server management panel
easy server reboot, OS reinstall, VNC access, API and etc.
-
security measures
two-factor authentication (2FA) for accessing the user panel, kernel updates for cloud servers and so on
8.  Pricing
Pricing
With a limited budget, be sure to review hosting pricing to avoid hidden costs or high-priced add-ons
-
pricing models
fixed pricing models are generally more affordable, while pay-as-you-go options offer greater flexibility
-
add-on/upgrade prices
some upgrades (for example adding 1TB of bandwidth) can be quite expensive
-
cost increase
LeaseWeb raises the cost of servers by a percentage of inflation almost every year
-
promotional codes
look for a promo code before making a payment, it can save you money over timeExamples:
- - promo code PROMO20 for 20% OFF for the monthly billing period at JustHost
- - promo code CHECK for 15% OFF on the first VPS or VPN order at THE.Hosting
9.  Support
Support
Hosting support is infrequent but crucial during urgent times. It's best to receive prompt and qualified assistance when resolving server issues.
- working time
- response time
- support channels (email, phone, tickets, live chat)
- migration help option
- knowledge base and tutorials
 Conclusion
Conclusion
When selecting a hosting company, there are various factors to consider; however, sometimes your options may be limited. Start by creating a list of your specific requirements and use it to filter potential hosting companies. Conduct thorough research on each company step by step, which includes a brief due diligence process. Check their reputation and read reviews, analyze any associated risks, assess additional parameters, and test the performance of their servers.
Some risks can be decreased if you have an infrastructure that allows you to migrate to another hosting provider semi-automatically without or with a short-term outage.
 Quiz
Quiz
Test your knowledge with the quiz:
-
Which country has the most data centers?
Top countries by data centers (by 2023 year): the USA, Germany, the UK, China, Canada, France, Australia, Netherlands, Russia, Japan
-
Choose the fastest type of storage device
PCIe NVME SSD is modern and several much faster than SATA SSD. HDD is a traditional storage device with low speed.
-
Choose the most suitable hosting solution for a long-term small project of your customer
It's better to use a stable hosting company with a qualified support and a guaranteed SLA for your customer's project.
-
Choose the hosting solution for a VPN server for a registered VPN business company
A young company in this case is also a risky option (they can block your server by a false abuse, shutdown quickly the business with no refund and etc.). So choose the first company. But for a new VPN provider with a modern infrastructure (fast deployment, server replacement in seconds and etc.) the second company could be an option for a time.
-
What is the year of building the first world's data center?
The world's first data centre (called a "mainframe") was created at the University of Pennsylvania to house the Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer (ENIAC) - the very first programmable, general-purpose, electronic digital computer ever created. The machine, which was formally dedicated in 1946, was 150 feet wide and required 150kW of power providing just 0.05 MIPS of computing power.
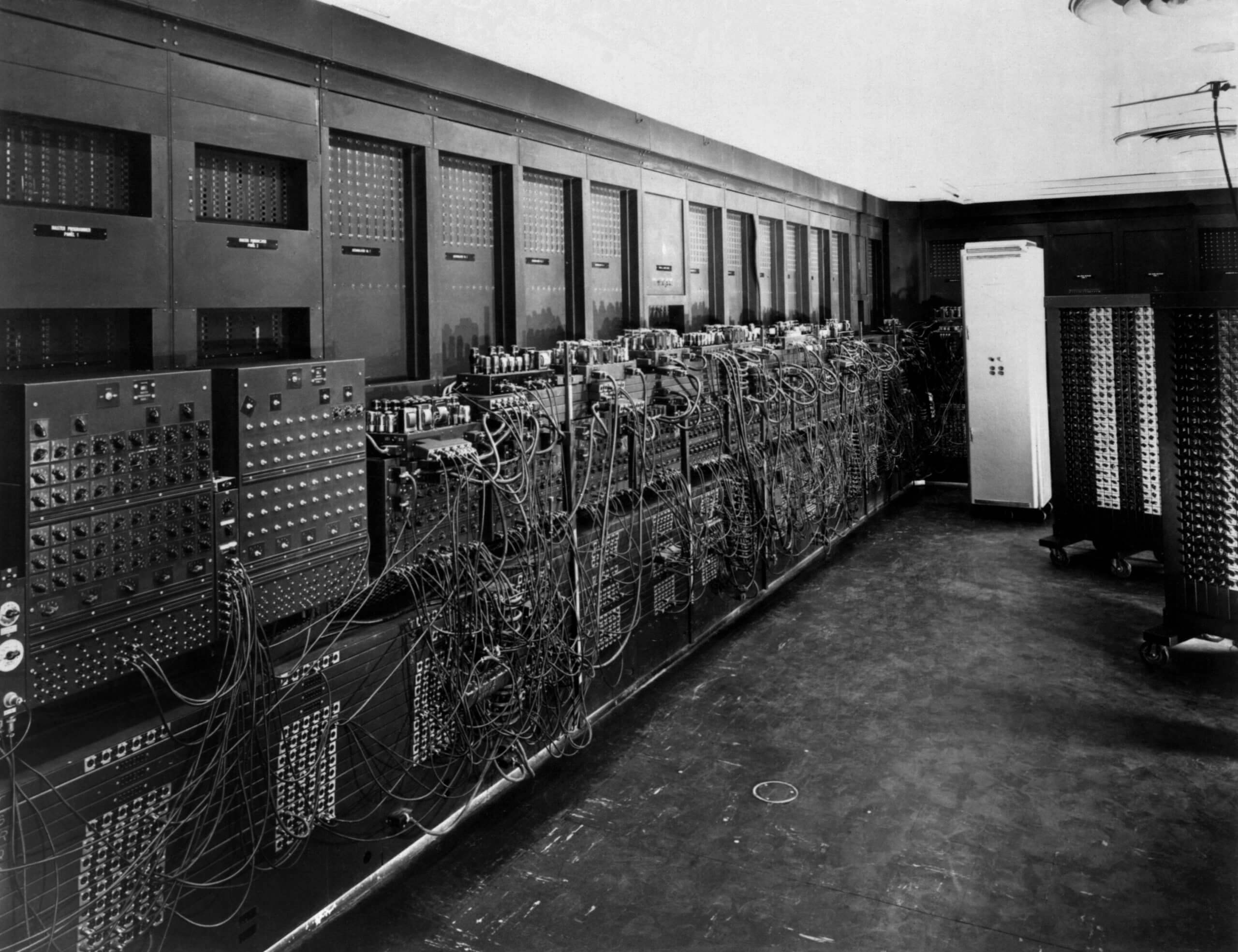 A part of Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer
A part of Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer -
What is the highest classification level for data centers?
Tier 4 has a full 2N+1 redundancy of all systems, including power supply and cooling distribution paths.
 Quiz results
Quiz results
 Top VPS, VPN, dedicated servers, and hosting in 40+ locations worldwide with JustHost — fast and reliable!
Top VPS, VPN, dedicated servers, and hosting in 40+ locations worldwide with JustHost — fast and reliable!